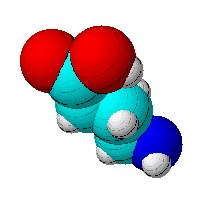
Lots of visitors to the sciencebase.com site search for “4-aminobutanoic acid” using the site’s Google search box. 4-aminobutanoic acid, or GABA, is (of course) the main inhibitor of neurotransmission in the central nervous system. According to Wikipedia, GABA is affected by drugs such as alcohol, benzodiazepines and barbiturates, thujone, zolpidem, and several others. You can see its chemical structure here. Click through this blog entry to read my recent chemistry news story for Reactive Reports on the subject of the GABA-A receptor and its role in catamenial epilepsy, a form of epilepsy that affects women during menstruation.