Rupert Sheldrake – Born: Newark-on-Trent, Notts, United Kingdom, June 28, 1942
Position: Fellow of the Sausalito, California Institute of Noetic Sciences, an independent research center studying consciousness and the nature of the mind.
Biography: Ph.D. in biochemistry as a Clare College research fellow. 1967-1973, director of studies in biochemistry and cell biology. 1970-1973, Royal Society fellow at Cambridge. 1974-1978, principal plant physiologist at the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in Hyderabad, India, and a consultant there until 1985. Frank Knox fellow, Harvard University fellow. Married to Jill Purce, with two sons; lives in London.
Sheldrake is quite well known in the United Kingdom as a maverick biologist because of his outspoken views on the nature of reality and, in particular, phenomena that are not usually considered “real” by science, such as the behavior of animals before an earthquake. His theory of morphic resonance, which he describes as “the basis of memory in nature,” might, he says, explain everything from the shapes of growing trees and phantom limbs to how homing pigeons home, as well as the animal-earthquake connection. But the theory has been the object of much scorn and derision from traditional scientific quarters because of its holistic and nondogmatic approach to nature. Sheldrake empathizes more, perhaps, with Alfred Russel Wallace than with Wallace’s more famous contemporary, Darwin. He believes that biology has lost sight of its holistic roots in its eagerness to provide a reductionist explanation of life.
Sheldrake’s latest book, Dogs That Know When Their Owners Are Coming Home: And Other Unexplained Powers of Animals (Crown, October 1999), seeks to explain animal and human behavioral phenomena that are considered to be outside the domain of conventional science. For instance, many people who have ever owned a pet will swear that their dog or cat or other animal has exhibited some kind of behavior that they just cannot explain. How does a dog know when its owner is returning home at an unexpected time? Sheldrake claims that his intensive research over the last five years demonstrates a strong connection between humans and animals that lies beyond present-day scientific understanding.
How would you describe yourself?
A biologist interested in exploring areas that lie beyond the boundaries of usual research.
What first inspired you to go into your field?
A love of animals and plants when I was a child, and a father who was an amateur naturalist who encouraged and nurtured my interest.
What do you enjoy about your work?
I can work freely and follow up any leads I find interesting because I work independently. I have been exploring unexplained areas of animal and human behavior, such as the feeling of being stared at from behind, which most people brush aside. I have done over 20,000 simple trials that suggest this is indeed a very real phenomenon.
Why do you think we have this “sense”?
I think it could have a major evolutionary role to play. For instance, if a prey animal can tell when a hidden predator is looking at it without being able to see, smell or hear it, then this would have survival value. Its presence in modern human beings may well be a relic of this.
So, what’s the explanation?
Conventional science cannot explain the effect, so it has been largely ignored. My own feeling is that morphic fields are involved.
What do you dislike about your research field?
There’s nothing wrong with the field of research as such, but most scientists don’t take it seriously, and there is no whole community working on these questions, so one sometimes feels isolated. Most of the time, that’s an advantage, because it’s much more exciting to explore uncharted territory rather than simply fill in the gaps in a heavily populated area of science. But I do miss some of the excitement of having a lot of bright colleagues engaged in similar research.
What aspects of science would you change if you could?
What upsets me most about science is the closed-minded dogmatism that is all too common, which makes a lot of scientists timid and afraid to go beyond convention. This affects cosmologists and physicists a lot less than biologists. After all, you can still be a cosmologist and speculate that the universe is one of an infinite number, or postulate extra dimensions of space and time. At one time, these were considered the realm of cranks, but now you can hold down a chair in a physics department. In biology, the atmosphere has become narrower and more intolerant as molecular biology and neo-Darwinism have squeezed out the traditional, holistic approach. Biology has become rather narrow and impoverished.
When did things change?
The craze for molecular biology and the success and excitement in that field have done a lot to draw attention away from whole organisms in favor of a more reductionist approach. This began in the 1920s, and the discovery of DNA carried the process further.
What was your first scientific experiment?
I must have been about seven or eight. I was fascinated by homing pigeons. I kept some, and my first experiment was to take one of them away and release it and find indeed that it came back.
How did the experience increase your maturity as a scientist?
I had no theory of my own at the age of seven or eight. But it showed me that pigeons seem to have knowledge of where they are in the world. All the scientific explanations put forward so far have been refuted experimentally, even the notion that a built-in “compass” may be the answer – knowing which way is north, after all, says nothing about where home is. It’s a problem that has stayed with me all my life, and I have never felt satisfied when people say it is just a matter of genes, proteins, or synapses.
What was your high-school science teacher like?
My biology teacher, Robin Thoday, was very inspiring. His father was a botany professor and his brother a geneticist, and he represented the older kind of biology, the traditional biology, where one actually knew the names of plants and animals and studied ecology. His approach encouraged me to look for explanations of things that were unexplained.
Was he a role model?
Not really. He was basically a teacher, and I saw myself in a research role. In a way I saw my father as a role model; he was an amateur microscopist and had his own laboratory at home.
What is your proudest achievement?
There is not a single one, but when I was researching plant development, I discovered that auxin, the plant hormone, is made by dying cells, which sheds tremendous light on the developmental biology of plants. Secondly, in India, working out the basic physiology of the crops I was working on and finding new ways to grow them with high yields. Thirdly, the development of the hypothesis of “formative causation,” which provides a larger framework for looking at nature.
What was your most embarrassing moment?
In India, I invented a new cropping system for growing pigeon peas as a perennial, and persuaded village farmers to take this up. It was a terrible failure because the peas were killed by disease that persisted on the perennial crop, which wouldn’t have happened if the crop had been grown in the traditional way. I did arrange for the institute to compensate the farmers, though.
What advice would you give a younger scientist?
If they are interested in making discoveries, then they should explore the unexplained in biology, where no one is working at the moment. I wouldn’t advise them to go into standard molecular biology, protein sequencing, genetic engineering. On the other hand, if they want a conventional career and to earn lots of money, that would be the way to go.
In what areas do you think you need advice yourself?
I work in quite a lot of different areas. In every area, I need advice from people such as statisticians, animal behaviorists, and psychologists, who have worked there longer than I have.
What would you be if not a scientist?
I haven’t a clue. I haven’t thought about being anything else since I was quite young, and I’m delighted I’ve been able to do what I wanted to do.
Who from scientific history would you like to meet?
The evolutionary biologist Alfred Russel Wallace. He’s one of my heroes. He had a much more far-ranging mind than Darwin, and while we know exhaustively about Darwin, we know very much less about Wallace.
What would you ask him?
I’d like to ask him about the biology of Southeast Asia, where he studied extensively. He also had a very different view of evolution than Darwin; he considered there to be creative forces at work rather than just blind chance, and I’d want to know why he thought it was necessary.
Which living scientist do you most admire?
James Lovelock.
Why?
Because of his independence and his ability to think in large-scale terms and not be put off by small-mindedness and petty criticisms.
What has been the greatest scientific discovery this century?
The discovery of the cosmic background microwave radiation, which led to the Big Bang theory. This transformed our fundamental cosmology from that of a static universe, or one slowly running out of steam and gave us instead an evolutionary vision of the whole of nature.
What will be the great discoveries of the next century?
The recognition of the nonlocal effects of the mind is going to transform our notion of consciousness and open up a whole new range of discovery about animal and human nature. This liberation will make science exciting again to lots of ordinary people.
What research goals do scientists need to set themselves?
I think I’d make a register of unexplained phenomena that scientists usually reject, to open up whole new areas of research into, for instance, the restlessness of animals immediately before earthquakes. I think at least 0.1% of science funding should go toward this.
Why do you think the public fears science?
It perceives it as arrogant and, with the GM controversy, it increasingly sees it as a corporate activity with scientists as hired hands rather than following science for its own sake.
What can scientists do to overcome this?
Make it more democratically accountable to the taxpayers, so that a polling system might bring to light the questions that people would really like to see answered. If science addressed interesting questions, it would increase science’s popularity and get children interested again. Research should relate to the problems that arise in our lives. The average person isn’t terribly interested in the genetic sequence of a bacterium or the existence or nonexistence of the Higgs boson, and yet this is where all the money goes in science.
This interview appeared on October 29, 1999, in David Bradley’s monthly BioFeedback column in the now defunct and much missed (not least for the monthly fee!) HMSBeagle on BioMedNet.

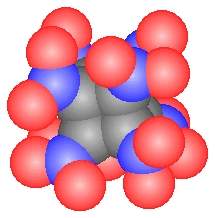 US chemists have synthesized a new type of explosive that could be more powerful than the most potent non-nuclear compound known.
US chemists have synthesized a new type of explosive that could be more powerful than the most potent non-nuclear compound known. Eaton and Zhang have developed a methodology involving non-standard procedures at each step to swap cubane’s corner hydrogen atoms with nitro groups – ultimately producing octanitrocubane. Nitro groups are common constituents of explosives for example in trinitrotoluene (TNT). The nitro groups provide oxygen for combustion of the carbon to carbon dioxide and release of nitrogen gas – explosively.
Eaton and Zhang have developed a methodology involving non-standard procedures at each step to swap cubane’s corner hydrogen atoms with nitro groups – ultimately producing octanitrocubane. Nitro groups are common constituents of explosives for example in trinitrotoluene (TNT). The nitro groups provide oxygen for combustion of the carbon to carbon dioxide and release of nitrogen gas – explosively.
 Evolutionary biologist Laura Landweber collaborated with computer scientist Richard Lipton, Dirk Faulhammer and Anthony Cukras to see whether they could solve a basic chess problem. The so-called ‘knight problem’ asks how many and where can one place knights on a chessboard so they cannot attack each other. Such a problem is known mathematically as an example of an ‘NP-complete’, which means the possible answers increase exponentially with increasing variables – in this case squares on the chessboard. The knight problem represents a class of mathematical problems that can best be solved by simple brute-force computation rather than a complex logical approach. So, to number crunch the problem, the team built a computational system from 1024 different strands of ribonucleic acid (RNA) combinations to look into this problem. Each strand of RNA represents a configuration of pairs of knights and to simplify the demonstration the system is equivalent to a nine-square chess board (3 x 3) so that there are a ‘mere’ 512 possible combinations of knights rather than the millions possible with a standard 64-square board.
Evolutionary biologist Laura Landweber collaborated with computer scientist Richard Lipton, Dirk Faulhammer and Anthony Cukras to see whether they could solve a basic chess problem. The so-called ‘knight problem’ asks how many and where can one place knights on a chessboard so they cannot attack each other. Such a problem is known mathematically as an example of an ‘NP-complete’, which means the possible answers increase exponentially with increasing variables – in this case squares on the chessboard. The knight problem represents a class of mathematical problems that can best be solved by simple brute-force computation rather than a complex logical approach. So, to number crunch the problem, the team built a computational system from 1024 different strands of ribonucleic acid (RNA) combinations to look into this problem. Each strand of RNA represents a configuration of pairs of knights and to simplify the demonstration the system is equivalent to a nine-square chess board (3 x 3) so that there are a ‘mere’ 512 possible combinations of knights rather than the millions possible with a standard 64-square board.
 Chemist Lloyd Smith and his colleagues have now shown they can attach a potentially computing set of DNA strands by one end to a gold-coated glass surface. They use their DNA-device to eliminate incorrect solutions from another NP-complete problem known as the satisfiability problem, which is essentially the knight problem phrased differently. By exposing the tethered strands to free-floating strands carrying sequences complementary to those satisfying each criterion met by the correct solution they could produce double helices. The incorrect solutions at each step are then exposed to a cleaving enzyme. Gentle heating regenerates single strands and the next DNA complement is added as the next criterion and so on. Decoding the single remaining double strands provides the problems solution.
Chemist Lloyd Smith and his colleagues have now shown they can attach a potentially computing set of DNA strands by one end to a gold-coated glass surface. They use their DNA-device to eliminate incorrect solutions from another NP-complete problem known as the satisfiability problem, which is essentially the knight problem phrased differently. By exposing the tethered strands to free-floating strands carrying sequences complementary to those satisfying each criterion met by the correct solution they could produce double helices. The incorrect solutions at each step are then exposed to a cleaving enzyme. Gentle heating regenerates single strands and the next DNA complement is added as the next criterion and so on. Decoding the single remaining double strands provides the problems solution.