 Canadian and Korean chemists have locked in a form of handedness into a common catalytic molecule that could make it useful for separating the building blocks of proteins, amino acids, into their chiral forms for biotech applications and drug development. The new locked up cat, might also be used to make purer and safer chemical starting materials for reactions in the drug, agrochemicals, and polymer industries.
Canadian and Korean chemists have locked in a form of handedness into a common catalytic molecule that could make it useful for separating the building blocks of proteins, amino acids, into their chiral forms for biotech applications and drug development. The new locked up cat, might also be used to make purer and safer chemical starting materials for reactions in the drug, agrochemicals, and polymer industries.
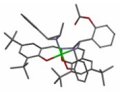
Jik Chin and colleagues at the University of Toronto, Canada, working with Jong-In Hong’s team at Seoul National University, Korea to synthesise a cobalt(III) complex of the ligand "salen". Salen is a commonly used ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is a Schiff base formed from a two to one reaction of derivatives of salicylaldehyde and ethylene diamine. Complexes of this ligand are very effective catalysts for a wide range of reactions including epoxidation of alkenes.
Read on…